TYPES OF GATING SYSTEM IN CASTING PROCESS
TYPES OF GATING SYSTEM IN CASTING PROCESS
- Mould is used for producing a casting. Molten metal is conveyed into the mold cavity by using Gating system. In casting process, gating system plays an important role to produce a high quality casting. A poorly designed gating system results in casting defects. A gating system controls mould filling process. The main function of gating system is to lead molten metal from ladle to the casting cavity ensuring smooth, uniform and complete filling.
Elements of Gating System
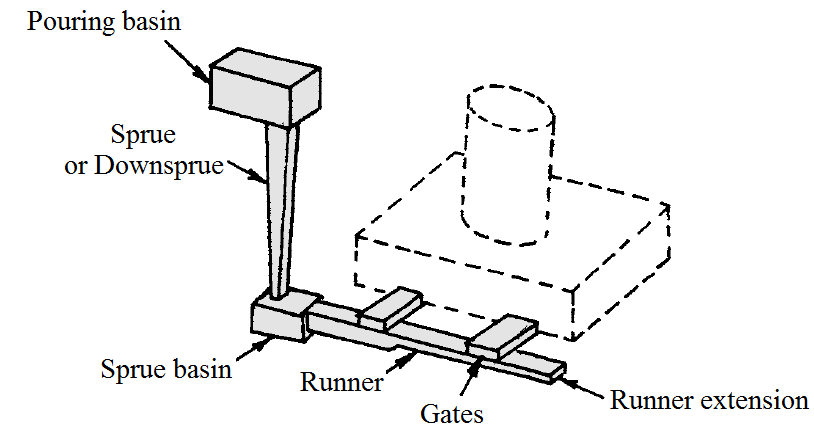
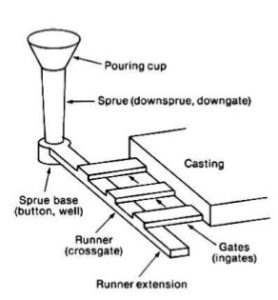
- Pouring Cup
- Spruce
- Spruce Well
- Cross-gate or Runner
- Ingate or Gates
- Pouring Cup – It is the funnel-shaped opening, made at the top of the mold. The main purpose of the pouring basin is to direct the flow of molten metal from ladle to the sprue.
- Spruce – It is a vertical passage connects the pouring basin to the runner or ingate. It is generally made tapered downward to avoid aspiration of air. The cross section of the sprue may be square, rectangular, or circular.
- Spruce Well – It is located at the base of the sprue. It arrests the free fall of molten metal through the sprue and turns it by a right angle towards the runner.
- Runner – It is a long horizontal channel which carries molten metal and distribute it to the ingates .It will ensure proper supply of molten metal to the cavity so that proper filling of the cavity takes place.
- Gate – These are small channels connecting the mould cavity and the runner.The gates used may vary in number depends on size of the casting.
- A good gating system should help easy and complete filling of the mould cavity.
- It should fill the mould cavity with molten metal with least amount of turbulance.
- It should prevent mould erosion.
- It should establish proper temperature gradient in the casting.
- It should promote directional solidification.
- It should regulate the rate of flow of metal into the mould cavity.
- Oxidation of metal
- Cold shuts
- Mould erosion
- Shrinkages
- Porosity
- Misruns
- Penetration of liquid metal into mould walls.
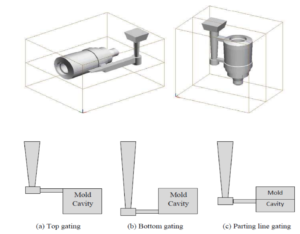
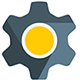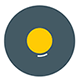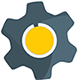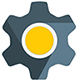
- Depending upon the orientation of the parting plane.
- Depending upon the position of ingate, horizontal gating system.
- Pouring rate is nothing but the time taken for filling the mould cavity by a known quantity of metal i.e., Pouring time can be used as an index to determine the pouring rate.
- When molten metal is being poured into the mould at a very fast rate, mould erosion, rough surface, excessive shrinkage may takesplace.
- When the pouring rate is very low, the complete filling of the mould is not assured and may result in excessive drop in the molten metal temperature.
- This result in casting defects such as cold shut, misrun etc.,
- In order to avoid this, it is necessary to arrive at the correct rate of pouring of metal into the mould cavity.
- The type of metal, size and shape of the casting decide the pouring rate.
- Gating ratio refers to the relation between area of the choke to total area of runner total area of Ingates. Mathematically, it can be written as Ac: Ar: Ag. The gating system completely controls the molten metal flow. Gating systems can be classified as Pressurised system and Unpressurised system. Gating ratio depends on the nature of the molten metal.
- Pressurized system is used for reactive metals like magnesium alloy etc. Unpressurised gating system is used for normal metals such as brass, steel, aluminium alloy, etc.
- A Gating ratio such as 1:2:1 or 1:0.75:0.5 refers to pressured system; whereas the gating ratio such as 1:2:2 or 1:3:3, 1:1:3, refers to unpressurised gating system.
- Pressurized system is referred to as “Gate control System”, since ingates controls the flow of metal.
- Unpressurised system is referred to as “Choke Control System”, since the choke controls the flow of metal.
- In the pressurized system high metal velocity occurs and results in turbulence. In the case of unpressurised system, turbulence is produced and streamline flow is induced.
- Pressurized System Consumes less metal and yield is more. Unpressurised system consumes more metal and the yield will be slightly lowered.
- In the case of pressurized system, the system will always be full of liquid metal . In the case of unpressurised system flow is not full.
- The size of the sprue fixes the flow rate. The amount of molten metal that can be fed into the mold cavity in a given time period is limited by the size of the sprue.
- The sprue should be located at certain distance from the gates
so as to minimize velocity of molten metal at ingates. - Sprue should be tapered by approximately 5% minimum to
avoid aspiration of the air and free fall of the metal. - Ingates should be located in thick regions.
- Locate the gates so as to minimize the erosion of the sand mold by the metal stream. This may be achieved by orienting the gates in the direction of the natural flow paths.
- Multiple gating is frequently desirable. This has the advantage of lower pouring temperatures, which improves the metallurgical structure of the casting. In addition, multiple gating helps to reduce the temperature gradients in the casting.
Function of Gating System
Defects occurring due to improper design of gating system
Types Of Gates
– Horizontal Gating System
-Vertical Gating System
-Top Gating System
-Bottom Gating System
-Parting-line Gating System